Introduction
India and Russia have recently taken their long-standing maritime cooperation to a new level. In December 2025, both nations signed multiple agreements including pacts on shipbuilding, polar seafarer training, and expanding strategic sea corridors.
This move promises to reshape India’s maritime landscape: from new Arctic-ready ships and trained crews capable of polar navigation to faster, more efficient trade routes between India, Russia, and beyond. In this article, we break down all key developments, explain why they matter, and what this means for India’s shipping industry written in simple language for students, maritime professionals, and all interested readers.
Why This Maritime Alliance Matters
Strengthening a Strategic Partnership
The two countries have reaffirmed what they call a “Special and Privileged Strategic Partnership,” aiming to expand cooperation across many sectors including trade, transport, energy, defence, and maritime.
Given changing global dynamics, India–Russia maritime cooperation offers strategic benefits: access to Arctic routes, expanded shipbuilding capabilities, and enhanced trade connectivity diversifying India’s global maritime options.
New Focus on Arctic & Polar Capabilities
One of the standout developments is the agreement for polar seafarer training. India and Russia signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to train Indian specialists for operating ships in polar waters a first-of-its-kind push for India.
This expands India’s maritime horizon beyond traditional tropical and temperate waters opening possibilities for Arctic shipping, polar cargo routes, and global maritime presence.

What Was Agreed – Key Areas of Cooperation
Polar Seafarer Training & Arctic-Ready Ships
- The MoU for training Indian sailors for polar waters aims to build capacity to navigate Arctic seas safely.
- Alongside training, both nations plan joint shipbuilding especially “Arctic-class” or “ice-class” vessels built to handle icy seas and harsh polar conditions.
- Russian expertise combined with Indian shipyard capacity could help India build vessels that meet global Arctic-shipping standards.
This dual focus human resource training and shipbuilding prepares India for polar operations in a concrete, practical way.
Enhanced Shipbuilding & Port Infrastructure Cooperation
Beyond ice-class vessels, the cooperation extends to broader shipbuilding and maritime infrastructure. Russia has offered collaboration to India to develop or build vessels (fishing, passenger, auxiliary) and improve port & maritime logistics infrastructure.
This could help upgrade India’s maritime fleet, reduce dependency on foreign vessels, and expand India’s shipbuilding capabilities under initiatives similar to “Make in India.”
New Trade Corridors: Faster, Strategic Maritime Routes
Two major maritime corridors are getting fresh momentum:
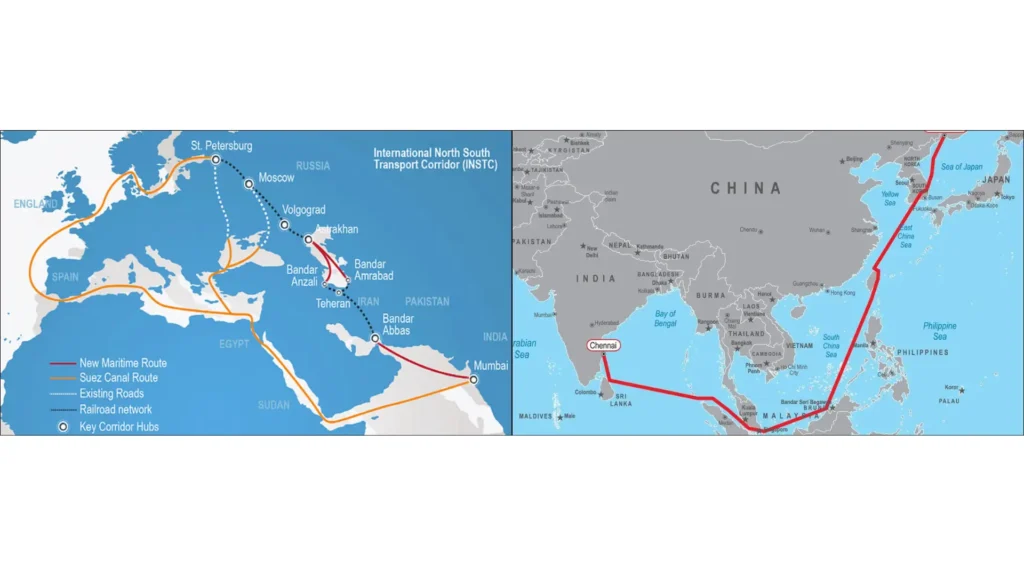
- The International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC) connecting India, Russia and beyond through ship, rail and road networks.
- The Chennai–Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (also called Eastern Maritime Corridor) a sea route linking Indian ports (like Chennai) with Russia’s Far East (Vladivostok), significantly cutting transit times.
With improved connectivity, logistics links and dedicated maritime infrastructure, cargo trade between India, Russia and partner regions could become faster, more efficient and more reliable. The corridors also support cargo, energy, and possibly polar-region shipping.
Broader Impacts – What This Means for India & Maritime Community
For Indian Seafarers & Maritime Workforce
- Sea-going crew will get opportunity to train for polar waters a unique skill set rarely available in India earlier. This could open new job opportunities, including Arctic or international polar-route shipping.
- With Arctic-class vessels, India’s merchant fleet may diversify creating demand for skilled sailors, navigators, engineers trained for cold climates and challenging navigation.
For Indian Shipbuilding Industry & Ports
- Collaboration with Russia could mean technology transfers, design sharing, and capacity building giving Indian shipyards a boost to build broader vessel types, from fishing/auxiliary to Arctic-class ships.
- Upgraded maritime infrastructure, port facilities, and improved logistics corridors may boost domestic shipbuilding demand and encourage maritime businesses.
For India–Russia Trade, Logistics & Global Reach
- Faster trade routes via INSTC and Chennai–Vladivostok corridor will reduce transit time and cost making India–Russia (and beyond) trade more competitive.
- Access to Northern Sea Route & Arctic shipping could link India to Europe, Arctic regions, and Eurasian markets more efficiently opening new trade, energy, and logistics possibilities.
- Diversification of shipping routes reduces dependence on traditional lanes, giving India strategic flexibility.
Strategic & Geopolitical Significance
- The cooperation strengthens India–Russia strategic ties, especially in maritime, transport, energy, and logistics sectors boosting long-term collaboration.
- Arctic & polar-capable fleet and trained manpower give India a presence in high-latitude maritime zones, enhancing its global maritime footprint and strategic autonomy.

Challenges and What Needs Attention
This cooperation is promising but there are hurdles and areas to watch:
- Infrastructure & Investment: Building Arctic-class ships, upgrading ports, and setting up logistics corridors will require heavy investment, technology transfers, and careful planning.
- Training & Skill Development: Polar navigation and Arctic operations demand specialized training, safety protocols, and readiness for harsh conditions. Implementing high-quality training will be key.
- Regulatory, Environmental & Safety Considerations: Arctic shipping comes with risks, ice-navigation hazards, environmental sensitivity, compliance with international maritime & environmental norms. Responsible implementation is vital.
- Coordination & Long-Term Commitment: Sustained cooperation between Indian & Russian agencies, shipyards, training institutes will be needed to deliver the full benefits. Half-measures or delays can undermine the potential.
- Global Geopolitics & Trade Dependencies: Given global geopolitical shifts, India must balance its maritime ambitions with diplomatic sensitivities, allied relations, and supply-chain resilience.
Conclusion
The recent India–Russia maritime alliance offers a bold new chapter in India’s maritime journey. With focus on polar seafarer training, Arctic-class shipbuilding, and strategic trade corridors like INSTC and Chennai–Vladivostok route India is not just strengthening bilateral ties but reimagining its global maritime presence.
For Indian seafarers, shipyards, maritime professionals, and policy-makers this means opportunity, a chance to train for polar waters, build advanced ships, and tap new global shipping lanes. But the success will depend on effective implementation, infrastructure investment, and sustained cooperation.
If done right, this alliance could transform India into a truly global maritime player bridging oceans, climates, and continents.
Source: PIB




